您當前的位置:檢測資訊 > 法規標準
嘉峪檢測網 2025-04-07 08:26
With the new chapter on Contamination Control Strategy (CCS), the USP builds a bridge between the requirements of CFR and the current 1st edition. In its introduction, the USP states that microbiological contamination control is a crucial part of drug manufacturing. In the USA, this is regulated by legal requirements such as CFR §211.113. A contamination control strategy (CCS) is required to minimise the risk of microbial contamination. It includes a holistic view of the entire production facility and is based on quality risk management (QRM). The most important sections are listed below, whereby the USP emphasises that this overview does not represent a 100% list of all relevant aspects.
近日,USP發布了關于污染控制策略 (CCS) 的新章節。USP 在其介紹中指出,微生物污染控制是藥物生產的關鍵部分。需要制定污染控制策略 (CCS) 以最大限度地降低微生物污染的風險。它包括整個生產設施的整體視圖,并基于質量風險管理 (QRM)。下面列出了最重要的部分,USP 強調,本概述并不代表所有相關方面的 100% 列表。
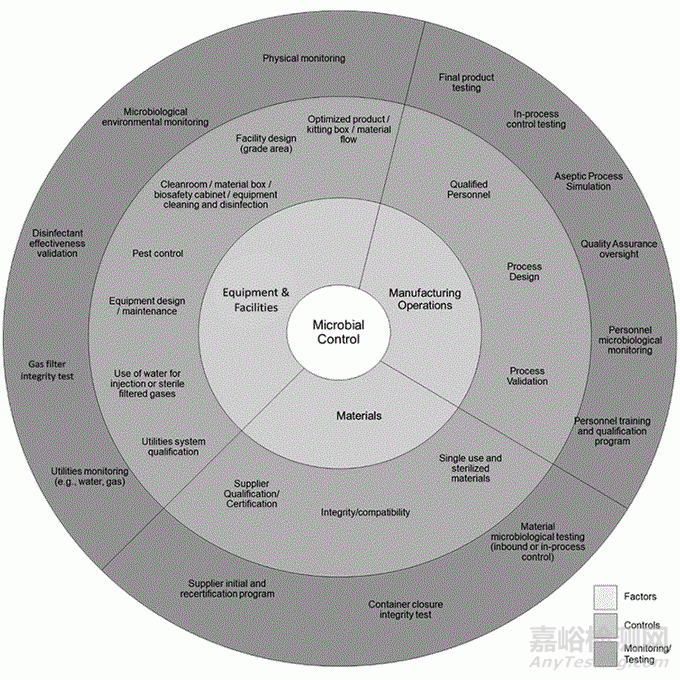
Planning and operation of the plant
廠房設計和運行
Cleanroom design: minimisation of microbial contamination through cascading pressurisation and appropriate cleanroom classifications (ISO standards).
潔凈室設計:通過壓差梯度和適當的潔凈室分類(ISO標準)最大限度地減少微生物污染。
Air control systems: Temperature, ventilation and humidity control, use of HEPA filters.
空氣控制系統:溫度、通風和濕度控制,使用 HEPA 過濾器。
Material flow & process flow: Unidirectional processes to avoid cross-contamination.
物流和工藝流:單向過程以避免交叉污染。
Cleanroom qualification: Regular testing of particles, airflow and filter integrity.
潔凈室確認:定期測試顆粒、氣流和過濾器完整性。
Maintenance: Planning of building maintenance taking microbial risks into account.
維護:廠房維護計劃考慮微生物風險
Equipment and process
設備和工藝
Equipment design: Cleanable and sterilisable production equipment with validated cleaning efficiency.
設備設計:可清潔和可消毒的生產設備,清潔有效性經過驗證。
Process design: Closed systems are preferred; open processes require ISO 5 environment.
工藝設計:首選密閉系統;開放式工藝需要 ISO 5 環境。
Material transfer: Validated methods for transfers to ISO 5 areas.
物料轉移:使用經過驗證的方法轉移到 ISO 5 區域。
Hold times: Must be validated to prevent microbial growth.
保持時間:應驗證以防止微生物生長。
Personnel
人員
Training: Fundamentals of microbiology, aseptic technique, environmental controls and cleaning.
培訓:微生物學基礎知識、無菌技術、環境控制和清潔。
Garbing: ISO 8 areas require protective suits, ISO 5 areas require additional sterile bonnets, masks and gloves.
著裝:ISO 8 區域需要防護服,ISO 5 區域需要額外的無菌頭罩、口罩和手套。
Qualification: Includes training, monitoring and microbiological testing.
確認:包括培訓、監測和微生物測試。
Supply facilities
公用設施
Water: Must be pharmaceutical grade and regularly tested for microbial contamination.
水:必須是制藥級的,并定期進行微生物污染檢測。
Process gases: Direct contact with products requires sterile filters (0.2 µm) and regular testing.
工藝氣體:與產品直接接觸需要除菌過濾器 (0.2 μm) 并定期測試。
Raw material controls
原輔料控制
Risk assessment: Takes into account origin, manufacturing processes and storage.
風險評估: 考慮源頭、生產工藝和儲存。
Incoming inspections: Inspection of materials by suppliers and manufacturers required.
入廠檢驗: 需要供應商和制造商對物料進行檢驗。
Product containers and closures
產品容器和密封部件
Integrity assurance: Container and closure integrity testing.
完整性保證:容器和密封部件完整性測試
Storage and transport validation: Ensuring microbial barrier function.
儲存和運輸驗證:確保微生物屏障功能。
Management of outsourcing activities
外包活動管理
Quality assurance of external service providers: audits, quality agreements and regular inspections.
外部服務提供商的質量保證:審計、質量協議和定期檢查。
Examples: Sterilisation, environmental monitoring and cleaning of outsourced areas.
示例:外包區域的清潔、消毒和環境監測。
Risk management and process validation
風險管理和工藝驗證
QRM approach: Identifying, analysing and assessing microbial risks.
QRM
方法:識別、分析和評估微生物風險。
Process validation: Continuous evaluation of sterilisation and production processes.
工藝驗證:對滅菌和生產過程進行持續評估。
Cleaning and disinfection
清潔和消毒
Regular disinfection: Based on cleanroom classification and microbial trends.
定期消毒:基于潔凈室級別和微生物趨勢。
Validation: Documentation of the effectiveness of cleaning agents and disinfectants used.
驗證:記錄所用清潔劑和消毒劑的有效性。
Verification of monitoring controls
監測措施的確認
Environmental and personnel monitoring: Evaluation of microbial control in production areas.
環境和人員監測:生產區域微生物控制評估。
Alternative monitoring methods: Faster detection of contamination using new technologies.
替代監測方法:使用新技術更快地檢測污染。
Trend analyses: To identify microbial hotspots and optimise the CCS.
趨勢分析:識別微生物熱點并優化 CCS。
Aseptic process simulations (APS)
無菌工藝模擬(APS)
Regular tests: Worst-case scenarios to ensure aseptic conditions.
定期測試: 在最差條件下測試以確保無菌條件
Validation of media fill tests: Proof of the effectiveness of the aseptic process.
培養基灌裝測試驗證:無菌工藝有效性的證明。
Investigation of deviations
偏差調查
Root cause analysis: Determining the cause of microbial contamination.
根本原因分析:確定微生物污染的原因。
Corrective and preventive actions (CAPA): Implementation and effectiveness testing.
糾正和預防措施 (CAPA):實施和有效性測試。

來源:Internet


