您當(dāng)前的位置:檢測資訊 > 科研開發(fā)
嘉峪檢測網(wǎng) 2021-08-16 13:46
藥品的生產(chǎn)制備、儲運(yùn)、使用的全生命周期過程,因微生物污染而導(dǎo)致藥物變質(zhì)的情況可能導(dǎo)致用藥安全問題,對藥品生產(chǎn)企業(yè)來說(尤其是無菌藥品),防污染是無菌藥品生產(chǎn)中必須確保的要素之一,因此防止及消除污染對于無菌藥品生產(chǎn)質(zhì)量保障來說至關(guān)重要,應(yīng)建立有效的污染控制策略(CCS)并進(jìn)行維護(hù)。本文分享了藥品污染控制策略(CCS)幾個關(guān)注的問題。
9月27-28日 CCS控制策略及風(fēng)險管理專題研修班 帶您全面解析CCS相關(guān)問題。
污染控制策略(CCS)為何物?
我們可以從2020年02月20日發(fā)布的EU GMP附錄《Manufacture of Sterile Products(無菌藥品生產(chǎn))》征求意見稿可以找到具體的定義:
Contamination Control Strategy (CCS) - A planned set of controls for microorganisms, pyrogens and particulates, derived from current product and process understanding that assures process performance and product quality. The controls can include parameters and attributes related to active substanc, excipient and drug product materials and components, facility and equipment operating conditions, in-process controls, finished product specification, and the associated methods and frequency of monitoring and control.
污染控制策略(CCS) - 來自于現(xiàn)行產(chǎn)品和工藝?yán)斫猓瑸榇_保工藝性能和產(chǎn)品質(zhì)量,所計(jì)劃的一套對微生物、熱源和微粒的控制。這些控制包括與原料藥、輔料、藥品的物料和組分、設(shè)施和設(shè)備操作條件、過程控制、成品質(zhì)量標(biāo)準(zhǔn)相關(guān)的參數(shù)和屬性,以及相關(guān)的監(jiān)測和控制的方法及頻次。
當(dāng)前國內(nèi)外污染控制策略(CCS)
法規(guī)對比分析
相比美國FDA和歐盟EU的GMP附錄,我國目前GMP法規(guī)未明確強(qiáng)調(diào)要求藥品生產(chǎn)企業(yè)制定書面的污染控制策略(CCS),但在2019年11月28日,國家藥品監(jiān)督管理局食品藥品審核查驗(yàn)中心官網(wǎng)重磅發(fā)布《GMP附錄-細(xì)胞治療產(chǎn)品》(征求意見稿),首次明確要求企業(yè)制定相應(yīng)的風(fēng)險控制策略,彌補(bǔ)了我國對藥品污染控制策略(CCS)法規(guī)層面的空白,國內(nèi)外污染控制策略(CCS)法規(guī)梳理總結(jié)對比如下表,從而更加直觀地比較中美歐藥品GMP關(guān)乎于CCS的監(jiān)管異同:
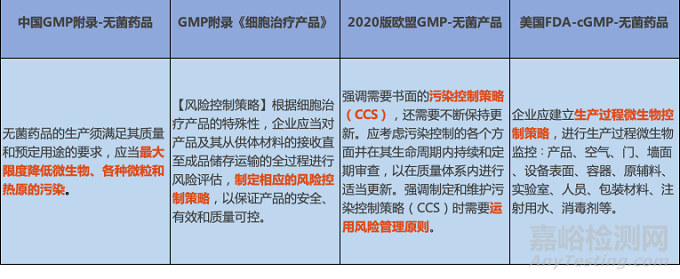
污染控制策略(CCS)
文件如何編寫
根據(jù)對于污染控制策略(CCS)的理解,CCS在我們的文件體系中,CCS可以是一個或多個文件,而且內(nèi)容非常龐大,建議以產(chǎn)品為主線去編寫自己企業(yè)的CCS,沒有一次就寫到最好的CCS文件,先按這個思路去思考、做出來,然后在實(shí)施的過程中,再根據(jù)認(rèn)知的提升、對風(fēng)險的思考的提升、對積累的數(shù)據(jù)的分析,不斷地更新文件,達(dá)到更好。
你得到的不是一個更好的CCS文件,而是一個更好、又更好的質(zhì)量保證狀態(tài)。污染控制策略(CCS)的污染控制策略應(yīng)考慮的要素包含(包括但不局限于):
i. Design of both the plant and processes.(廠房和工藝的設(shè)計(jì))
ii. Premises and equipment.(廠房設(shè)施和設(shè)備)
iv. Personnel.(人員)
v. Utilities.(公用系統(tǒng))
vi. Raw material controls – including in-process controls.(起始物料的控制-包含中間控制)
vii. Product containers and closures.(產(chǎn)品包裝)
viii. Vendor approval – such as key component suppliers, sterilization of components and single use systems (SUS), and services.(供應(yīng)商的批準(zhǔn)-例如關(guān)鍵組分的供應(yīng)商、部件的滅菌及一次性使用系統(tǒng)(SUS)和服務(wù)。)
ix. For outsourced services, such as sterilization, sufficient evidence should be provided to the contract giver to ensure the process is operating correctly.(對于委托外部的服務(wù),例如滅菌,應(yīng)將充分的證據(jù)提供給合同的委托方,以確保工藝的正確操作。)
x. Process risk assessment.(工藝風(fēng)險評估)
xi. Process validation.(工藝驗(yàn)證)
xii. Preventative maintenance–maintaining equipment, utilities and premises (planned and unplanned maintenance) to a standard that will not add significant risk of contamination.(預(yù)防性維護(hù)保養(yǎng)-設(shè)備,公用系統(tǒng)及設(shè)施的維護(hù)保養(yǎng)(計(jì)劃性及非計(jì)劃性維護(hù)保養(yǎng))符合標(biāo)準(zhǔn),不會加大顯著的污染風(fēng)險。)
xiii. Cleaning and disinfection.(清潔和消毒)
xiv. Monitoring systems-including an assessment of the feasibility of the introduction of scientifically sound, modern methods that optimize the detection of environmental contamination.(監(jiān)測系統(tǒng)-包括對引入檢測方法的可行性評估,方法科學(xué)合理,現(xiàn)代化,能夠優(yōu)化環(huán)境污染的檢測。)
xv. Prevention-trending, investigation, corrective and preventive actions (CAPA), root cause determination and the need for more comprehensive investigational tools.(預(yù)防措施-趨勢分析、調(diào)查、糾正和預(yù)防措施(CAPA)、根本原因的確定以及需求更全面的調(diào)查工具。)
xvi. Continuous improvement based on information derived from the above.(基于來自上述衍生信息的持續(xù)改進(jìn)。)
參考文獻(xiàn)
EU GMP 附錄1《Manufacture of Sterile Products(無菌藥品生產(chǎn))》

來源:Internet


